Endoscopy is a modern highly informative method of instrumental diagnostics, which is an examination of body cavities with an endoscope, which allows obtaining an accurate, large-scale and high-quality image of the area being examined. Which allows you to visually assess the condition of the abdominal organs and tubular organs, identify foci of inflammation, bleeding, erosion, as well as diagnose cancer at an early stage. Special endoscope tips are used to remove foreign bodies, take samples for biopsy (taking biological material from suspicious areas), extract polyps, etc.
The following endoscopic examinations are carried out at the MediClub:
■ Arthroscopy – a method of examination of the joints;
■ Bronchoscopy – a method of examination of the respiratory tract;
■ Gastroscopy – a method of examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract;
■ Hysteroscopy – a method of examination of the uterine cavity;
■ Colonoscopy – a method of examination of the colon;
■ Sigmoidoscopy – a method of examination of the rectum and distal sigmoid colon;
■ Cystourethroscopy – a method of examination of the urinary system;
■ Endoscopy of ENT organs.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive endoscopic method for the diagnosis and surgical treatment of joint injuries.
The essence of the method lies in the fact that the arthroscope is inserted into the joint cavity through 2 small incisions, which allows you to fully examine the joint, obtain information about its condition and identify the presence of intra-articular damage.
Arthroscopy allows you to assess the condition of the articular cartilage, ligaments, synovial capsule, tendons, upper lip; to detect intra-articular adhesions, scars, exostoses, as well as blood (hemarthrosis) or joint effusion.
Arthroscopy allows arthroscopic treatment of injuries of the knee joint. This technique allows you to remove the damaged part of the meniscus, restore ligaments, damaged cartilage and perform many other surgical interventions.
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the upper and lower (trachea, bronchi) respiratory tract using a bronchoscope. Bronchoscopy allows you to examine the bronchial mucosa, identify pathological changes in the lungs and bronchi, diagnose cancer at an early stage, remove a foreign body from the bronchi and trachea, and take samples for biopsy. Bronchoscopy is also the most important and effective method of treating patients with chronic inflammatory and purulent lung diseases.
Gastroscopy
Gastroscopy (EGDS, FGDS, esophagogastroduodenoscopy) is an endoscopic examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract using a gastroscope. On examination, the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum are examined.
This is an indispensable diagnostic method for esophagitis, gastritis, duodenitis, peptic ulcer, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), duodenogastric reflux, oncological diseases of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum in the early stages, gastrointestinal bleeding. If a suspicious area of the mucosa is found during the examination, a sample (biopsy) can be taken for a detailed examination of the tissue. Also, a modern endoscope makes it possible to remove polyps and treat erosions of the mucous membranes of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
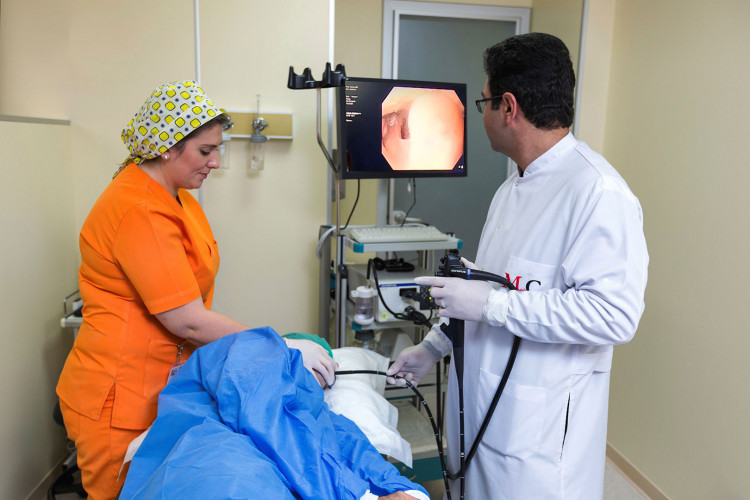
Standard gastroscopy usually includes a test for Helicobacter pylori - a urease test. Helicobacter pylori is a spiral bacterium that infects the mucosa of the pyloric stomach and duodenum.
Strains (species) of H. pylori differ in their ability to attach to the mucous membrane, cause an inflammatory process, and have varying degrees of pathogenicity.
Diseases associated with H. pylori are gastritis, duodenitis, peptic ulcer, gastric and duodenal cancer.
This bacterium is 100% detected during gastroscopy, for which a biopsy is taken during the study.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a method of endoscopic examination of the uterine cavity using a hysteroscope. Hysteroscopy is carried out both for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes (target biopsy of the endometrium, removal of polyps, separation of intrauterine synechia (unions in the uterine cavity), etc.)
Indications for hysteroscopy are: suspicion of endometrial pathology according to ultrasound or hysterosalpingography (endometrial polyp, endometrial hyperplasia), uterine bleeding (dysfunctional, postmenopausal, etc.), intrauterine synechia, submucosal uterine myoma, suspicion of malformation of the uterus (intrauterine septum, dimetria etc.), built-in intrauterine device (IUD), miscarriage, several unsuccessful attempts at in vitro fertilization (IVF), screening of the uterine cavity in the subsequent before surgical or hormonal treatment.
Hysteroscopy allows for operations with minimal trauma to the inner walls of the uterus, which is especially important for women planning a pregnancy.
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the colon using a colonoscope.
Colonoscopy is the most accurate diagnostic method for malignant and benign neoplasms of the rectum and colon, nonspecific inflammatory diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease), as well as congenital anomalies of the colon.
Indications for diagnostic colonoscopy are: blood in the feces, chronic diarrhea and constipation, abdominal pain along the colon, bloating, subfebrile condition (increased body temperature over a long period of time) of unknown origin, weight loss, anemia of unknown origin, sensation of a foreign body in the rectum, evaluation of the effectiveness of conservative or surgical treatment, diagnosis of tumors, polyps and other neoplasms in relatives over 45 years of age (in order to prevent colon cancer).
In necessary cases, this diagnostic method allows for a targeted biopsy of a site that is suspicious for further histological examination.
Rectosigmoidoscopy
Rectosigmoidoscopy is a method of endoscopic diagnosis of the condition of the mucous membranes of the rectum and distal sigmoid colon using a rectosigmoidoscope.
This method does not involve the assessment of the mucous membrane of the blind, ascending, transverse and descending colon, while the pathological process can be localized in these unexplored areas. In this regard, if necessary, depending on the identified changes, the examination can be extended to a total colonoscopy.
Cystourethroscopy
Cystoureteroscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the urethra and bladder using a cystoscope.
The method allows assessing the condition of the mucous membranes of the urethra and bladder, identifying foci of the inflammatory process, calculi, diverticula and fistulas of the bladder, urethral stricture, neoplasms.
Cystoureteroscopy can be performed in the following conditions: hematuria (blood in the urine), pyuria (pus in the urine), difficulty urinating, pain when urinating, enuresis (bedwetting), suspected neoplasm.
With cystoscopy, tissue biopsy is available for further histological examination, it can also be performed for therapeutic purposes: coagulation (cauterization) of ulcers, removal of polyps, lithotomy, catheterization and stenting of the ureter, administration of drugs, etc.
Diagnostic cystoscopy is performed under local anesthesia. If the procedure involves therapeutic manipulations, other types of anesthesia can be used.
Endoscopy of ENT organs
Video endoscopy of ENT organs is a method of endoscopic examination of the nasal cavities, nasopharynx, pharynx, larynx using an endoscope. The camera located at the tip of the endoscope allows the ENT doctor to view the mucous membrane of the organ under study on the monitor screen.
This study allows you to determine the exact cause of nasal congestion, assess the size of the adenoids, examine the shape, size and patency of the turbinates, examine the mouths of the Eustachian tubes, assess the condition of the vocal cords, detect a tumor process in the cavity of the ENT organs, etc.
Endoscopy of ENT organs in the Polyclinic MediClub is carried out using the latest equipment. The procedure is fast (10-15 minutes), painless, highly informative and does not require special preparation.
