Computed tomography
Computed tomography (CT) is a method of radiation diagnostics used for a thorough examination of internal organs, bones, soft tissues and blood vessels. The method is based on the use of X-ray flux.
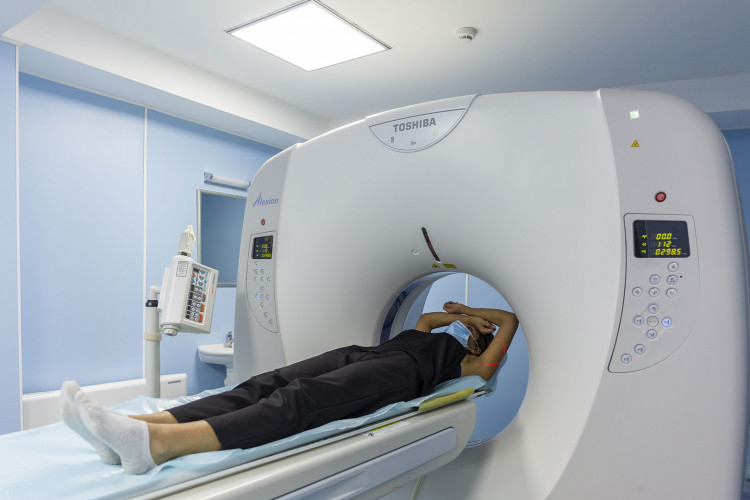
Unlike conventional x-rays, computed tomography provides a very extensive view of various tissue types, as well as lungs, bones, and blood vessels, providing real-time imaging. This is especially true for procedures involving the lungs, abdomen, pelvis, and bones. Diagnosis based on CT scan results may eliminate the need for exploratory surgery or biopsy.
Computed tomography is often considered the best way to diagnose various cancers, as imaging allows you to determine the tumor, its location and size.
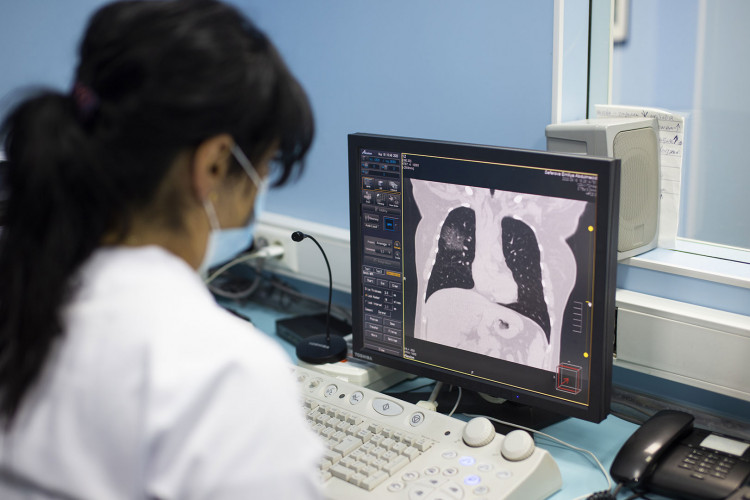
Due to the short time of this procedure and its simplicity, computed tomography has firmly occupied a niche in emergency medicine, where every second counts. In such cases, CT is used to determine internal damage or bleeding.
Computed tomography is necessary for pathologies of the lungs, mediastinal organs, brain and spinal cord, neck vessels and large vessels, ENT organs, spine, liver, kidneys, pancreas, pelvic organs and other pathologies that require a more detailed examination before the initial examination. completed.
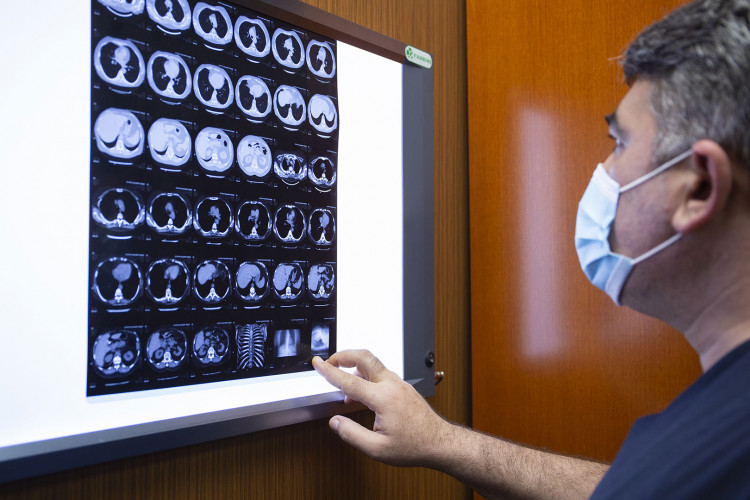
A contraindication for CT is pregnancy of any term. Infants are indicated only when no other study is applicable.
In addition to native (contrast-free) CT performed with contrast, CT allows you to accurately visualize the vascular fold, determine areas of expansion or narrowing, diagnose vascular occlusion, neoplasms, assess the condition of the cavitary and parenchymal organs of the small pelvis and bowl, etc.
In the MediClub, CT is performed at the MediClub Hospital using a Toshiba Alexion machine (Japan). The radiologist determines the required volume and rational method of research. Images are available on the computer screen, in printed form and on electronic media. CT is speed, painlessness, non-invasiveness and accuracy.
Radiography
Radiography is a method of radiation diagnostics. Modern digital X-ray equipment provides visualization of the smallest details and allows you to reliably determine all the features of the organ under study.
MediClub clinics conduct X-ray examinations in accordance with the list below:
■ Planned radiography (radiography of the skull, chest organs, abdominal organs, limbs);
■ X-ray of soft tissues (muscles, tendons, ligaments);
■ Sighting radiography (sighting is performed using special nozzle narrowing of the x-ray flow. It is used mainly in dentistry.);
■ Radiography of the spine with functional tests (standard radiography includes two images: anterior and lateral projections. Functional tests require changes in the position of the spine (deviations). Changes in the position of the vertebrae and the spine as a whole allow more accurate diagnosis of a number of diseases, including osteochondrosis, disc herniation;
■ Panoramic radiography (allows for a detailed visualization of the organ under study in a single image). Most commonly used in dentistry;
■ HSG (hysterosalpingography) - X-ray examination of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes.
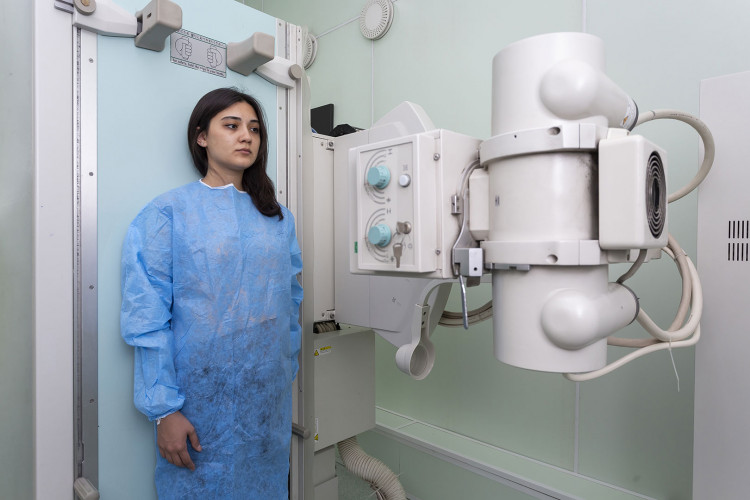
Modern digital X-ray machines SHIMADZU (Japan) in the clinic and AGFA DR 100e (USA) in the hospital allow high-definition and high-quality video recording. All images are stored in a computer database, available for printing when needed.
There are also two portable x-ray machines in the X-ray department of the MediClub, which ambulance doctors use to examine at home non-transportable patients or patients with disabilities.
